Modal verbs can be used to express preference, indicating what we would rather choose or do.
Modal verbs are a big part of everyday English, and they’re especially handy for ESL learners looking to express themselves more naturally. These verbs – like can, could, might, and should – help you talk about possibilities, give advice, and even make polite requests. On this page, we’ll dive into the rules for using modal verbs correctly, explore plenty of examples, and give you a chance to practice so you can feel confident using them in conversations. Ready to master modals? Let’s get started!
Understanding the Meaning of Modal Verbs in English
A modal verb is a type of auxiliary (or “helping”) verb, also known as a “modal auxiliary.” Modals are used to express specific ideas like:
- ability
- intention
- obligation
- necessity
- permission
- possibility
Unlike regular verbs, modal verbs don’t follow standard conjugation rules; instead, they directly modify the meaning of main verbs in a sentence, adding an extra layer of expression. Examples of modal verbs include can, could, may, might, should, and must. These verbs help create more precise and flexible sentences, making them essential for clear communication in English.
Modal Verbs List
Modal verbs are essential in English, as they help express various meanings such as ability, necessity, and possibility. Here are some of the most common modal verbs you’ll encounter and their uses.
- can
used to express – ability, permission, possibility, request - could
used to express – ability, permission, possibility, request, suggestion - have to
used to express – obligation, necessity, advice, persuasion - may
used to express – permission, possibility, probability, request - might
used to express – possibility, small probability, request - must
used to express – obligation, necessity, certainty, advice, prohibition - need
used to express – necessity, obligation, lack of necessity - ought to
used to express – advice, obligation, opinion, recommendation - shall
used to express – offers, suggestions, future intentions, questions - should
used to express – advice, obligation, opinion, recommendations - will
used to express – future intentions, offers, promises, predictions - would
used to express – requests, hypothetical situations, past habits, offers, questions
Let’s delve a little deeper and see some examples.
Modal Verb Examples
Modal verbs are essential in English, helping us express things like ability, permission, and possibility. Below, you’ll find some common modal verbs with examples to show how they’re used in everyday speech.
Using ‘Can’ to Express Ability, Permission, Possibility, and Requests
Can’ is a versatile modal verb in English. It’s used to talk about ability, like “She can speak three languages,” permission, as in “Can I borrow your pen?”, possibility, such as “It can get really cold here in winter,” and making requests, like “Can you help me with this?” Its flexibility makes it an essential part of everyday conversation.
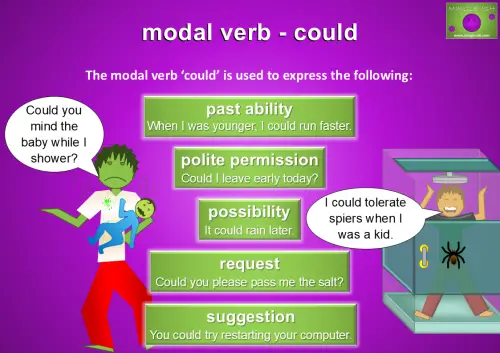
Using ‘Could’ to Express Ability, Permission, Possibility, Requests, and Suggestions
Could’ is a flexible modal verb used in various ways. It expresses past ability, like “When I was younger, I could run faster,” polite permission, such as “Could I leave early today?”, possibility, like “It could rain later,” requests, as in “Could you please pass me the salt?”, and suggestions, like “You could try restarting your computer.” Its many uses make it an essential part of everyday conversation.
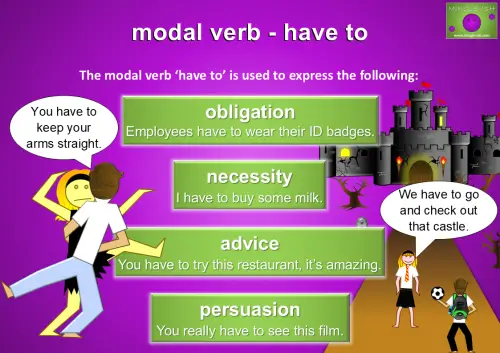
Using ‘Have To’ to Express Obligation, Necessity, Advice, and Persuasion
Have to’ is often used to talk about obligations, such as “Employees have to wear their ID badges at all times.” It’s also used for things that are necessary, like “I have to buy some milk; we’re completely out.” Additionally, it’s great for giving advice, like “You have to try this restaurant; it’s amazing,” or persuading someone, as in “You really have to see this film!” Whether discussing requirements or making strong recommendations, ‘have to’ is incredibly versatile.
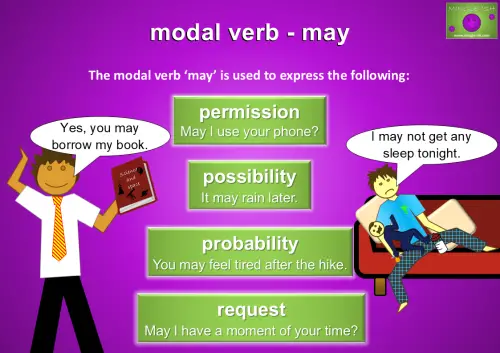
Using ‘May’ to Express Permission, Possibility, Probability, and Requests
‘May’ is a formal modal verb used for asking or giving permission, like “May I use your phone?” It’s also used to express possibility or probability, such as “It may rain later” or “You may feel tired after the hike, so plan to rest.” Additionally, ‘may’ adds a polite tone to requests, like “May I have a moment of your time?” making it ideal for respectful and courteous communication.
Using ‘Might’ to Express Possibility, Probability, and Requests
‘Might’ is a modal verb used to express possibility or probability, like “It might snow tomorrow” or “She might already be on her way.” It can also add a polite tone to requests, such as “Might I ask you a question?” While ‘might’ and ‘may’ are similar, ‘might’ often suggests a lower level of certainty, making it great for showing doubt or politeness.
Using ‘Must’ to Express Obligation, Necessity, Certainty, Advice, and Prohibition
‘Must’ is a powerful modal verb used to express obligation or necessity, like “Hikers must stick to the paths”, or “You must wear a seatbelt while driving.” It also conveys certainty, as in “That must be your sister; you look so alike!” and strong advice, such as “You must try this cake; it’s incredible!” Additionally, ‘must not’ is used to express prohibition, for example, “You must not smoke in this area.” Its versatility makes it essential for emphasising rules, confidence, and urgency.
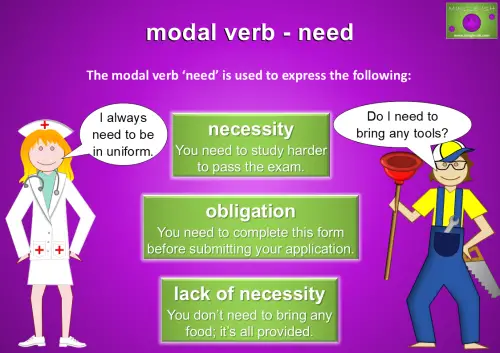
Using ‘Need’ to Express Necessity, Obligation, and Lack of Necessity
‘Need’ is a modal verb used to express necessity, as in “You need to study harder to pass the exam,” or obligation, like “You need to complete this form before submitting your application.” It’s also commonly used in the negative to show a lack of necessity, such as “You don’t need to bring any food; it’s all provided.” ‘Need’ is straightforward and practical for highlighting what’s required – or not – in various situations.
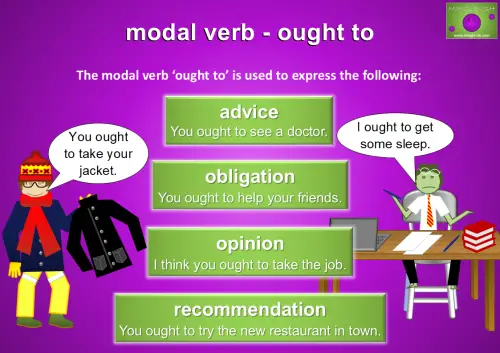
Using ‘Ought To’ to Express Advice, Obligation, Opinion, and Recommendation
‘Ought to’ is a modal verb used to give advice, like “You ought to see a doctor if you’re feeling unwell,” or to express obligation, such as “You ought to help your friends when they ask.” It can also be used to share an opinion, like “I think you ought to take the job,” and to make a recommendation, such as “You ought to try the new restaurant in town.” While similar to ‘should,’ ‘ought to’ is a bit more formal and often used for stronger suggestions or opinions.
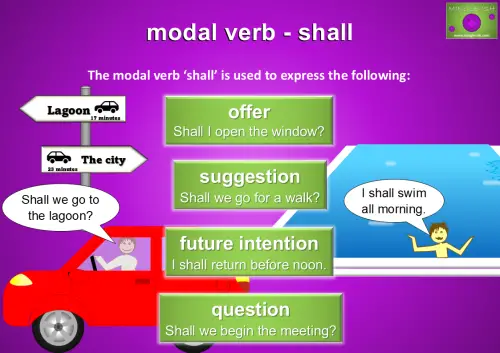
Using ‘Shall’ to Express Offers, Suggestions, Future Intentions, and Questions
Shall’ is a formal modal verb used to make offers, like “Shall I open the window?” or to suggest something, such as “Shall we go for a walk?” It’s also used to express future intentions, as in “I shall return before noon.” Additionally, ‘shall’ is commonly used in questions, especially in formal or polite contexts, like “Shall we begin the meeting?” While less frequent in casual conversation, ‘shall’ is still widely used in formal settings or when making polite suggestions or offers.
Using ‘Should’ to Express Advice, Obligation, Opinion, and Recommendations
‘Should’ is a versatile modal verb used to give advice, like “You should see a dentist if you’re feeling unwell.” It can also express obligation, such as “You should complete the report by tomorrow.” Additionally, ‘should’ is commonly used to share an opinion, like “I think you should move to the south,” or to make recommendations, such as “You should try the vegan lasagne.” While it’s a bit less forceful than ‘must,’ ‘should’ is a practical and widely-used modal verb for offering guidance or making recommendations.
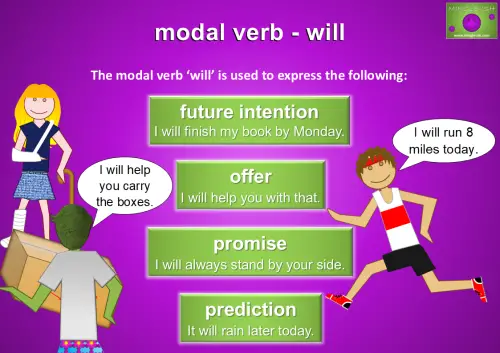
Using ‘Will’ to Express Future Intentions, Offers, Promises, and Predictions
‘Will’ is a versatile modal verb used to express future intentions, like “I will finish my book by Monday.” It’s also commonly used for making offers, such as “I will help you with that,” and to make promises, like “I will always stand by your side.” Additionally, ‘will’ is often used to make predictions, as in “It will rain later today.” Whether it’s about future plans, offering assistance, or predicting outcomes, ‘will’ is a key verb for talking about what’s to come.
Using ‘Would’ to Express Polite Requests, Hypothetical Situations, Past Habits, Offers, and Questions
‘Would’ is a modal verb used to make polite requests, like “Would you mind helping me with this?” It’s also used for hypothetical situations, such as “I would travel more if I had the time.” Additionally, ‘would’ can describe past habits, like “When we were kids, we would play outside for hours,” and is used for making offers, such as “I would be happy to assist you.” ‘Would’ is also commonly used in questions, like “Would you like some coffee?” or “Would it be okay if I left early?” Whether for politeness, possibilities, or past actions, ‘would’ is a versatile verb in English.
Different Uses of Modal Verbs with Examples
Modal verbs are super handy in English, helping us express things like ability, permission, obligation, and probability. They change meaning depending on the context, making them really flexible. Here, we’ll break down the different uses of modal verbs with examples to show how they work in everyday sentences.
Ability
Modal verbs can be used to express ability, indicating what someone can do or is capable of doing.
- I can play the piano quite well.
- She could solve complex puzzles when she was a child.
- With enough practice, he will be able to run a marathon next year.
Advice
Modal verbs can be used to give advice, offering suggestions or guidance to someone.
- You should see a doctor if your headache doesn’t improve.
- You ought to drink more water to stay hydrated.
- You have to start revising now if you want to pass the exam.
Assumption
When making assumptions, we use modal verbs to express what we believe is true based on available information.
- Must be at work by now; she left an hour ago.
- He might be at the party; I haven’t seen him yet today.
- They should have finished the project by now; the deadline was last week.
Certainty
When expressing certainty, we use modal verbs to show that we are sure about something.
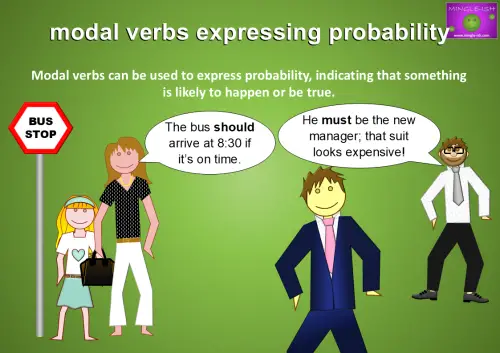
- She must be the new manager; I saw her in the office yesterday.
- He will definitely pass the exam; he’s been studying for weeks.
- They can’t be serious about quitting their jobs; they love working here.
Deduced conclusions
Modal verbs can be used to express deduced conclusions, where we make logical guesses based on available evidence.
- She must be the one who left the note; her handwriting is all over it.
- The lights are off, so they can’t be home right now.
- He might be the one who took the last cookie; I saw him near the jar earlier.
Deduction
Modal verbs can be used to express deduction, where we make logical conclusions about something based on evidence or reasoning.
Emphasis (for certainty)
Expectation
Modal verbs can be used to add emphasis for certainty, stressing how sure we are about something.
Expressing doubt
Modal verbs can be used to express doubt, where we show uncertainty about something.
Expressing preference
Future predictions
Habitual actions in the past
Habitual behaviour (present)
Hypothetical situations
intentions
Lack of obligation
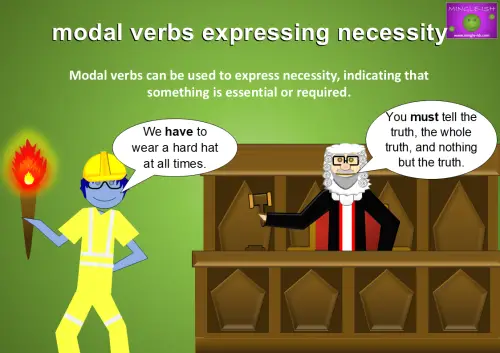
Necessity
Obligation
Offers
Permission
Polite language
Polite refusal
Possibility
Probability
Promises
Prohibition
Reluctance
Requests
Suggestions
Uncertainty
Willingness
Common Modal Verbs and their Functions
Now that you understand what a modal verb is, click on the headings below to dive deeper into each one. You’ll find their meanings, uses, and picture examples to help clarify how they function in English.
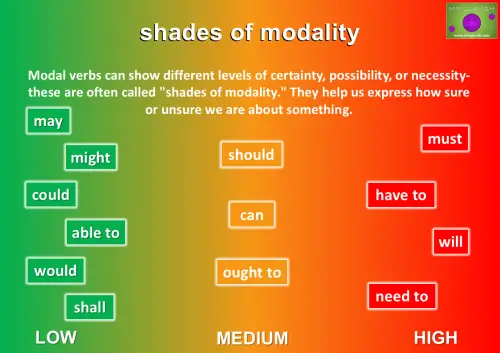
Shades of Modality
Modal verbs show different levels of possibility, probability, or necessity, which is why they’re sometimes called “shades of modality.” They let you express how certain, likely, or required something is, from a definite yes to just a maybe.
Top Tips and Rules for Modal Verbs
Mastering modal verbs is key to sounding natural and confident in English. These versatile little words can express everything from ability and possibility to obligation and advice. With the right approach, you can use them clearly and effectively in both speech and writing. Here are some top tips to help you get it right!
‘Need’ and ‘ought’ must be followed by ‘to + infinitive’.
For example:
- I ought to start eating healthier.
- I need to take him to the vet immediately.
The infinitive always follows a modal (not the other way around).
For example:
- We need to save our planet.
- We should call in sick today.
The perfect form for a modal is: modal + have + participle
For example:
- We were only a minute late; We couldn’t have missed the bus.
- I should have brought my ladder.
The continuous form for a modal is: modal + be + verb + ing
For example:
- I will be sleeping in this windmill for the next 3 nights.
- I could be staying up late tonight.
Don’t use the auxiliary ‘do’ with a modal for questions and negatives.
For example:
- Do you can help us with the cleaning? WRONG
- Can you help us with the cleaning? RIGHT
- She doesn’t can swim. WRONG
- She can’t swim. RIGHT
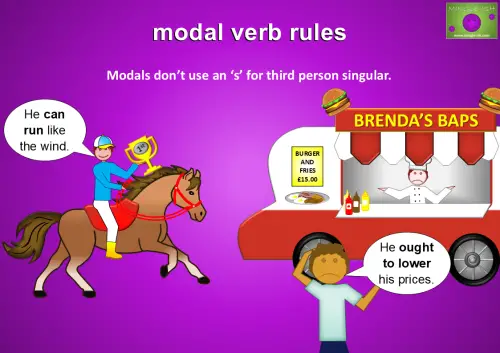
Modals don’t use an ‘s’ for third person singular.
For example:
- He can run like the wind.
- He ought to lower his prices.
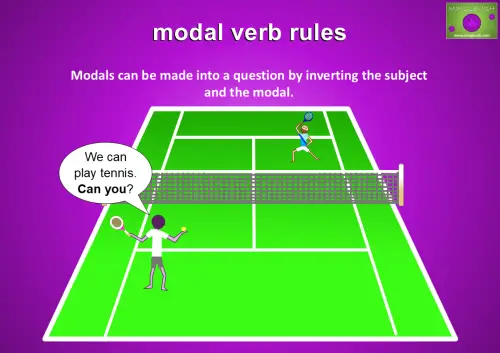
Modals can be made into a question by inverting the subject and the modal.
For example:
- We can play tennis. Can you?
- I would like a cup of tea. Would you?
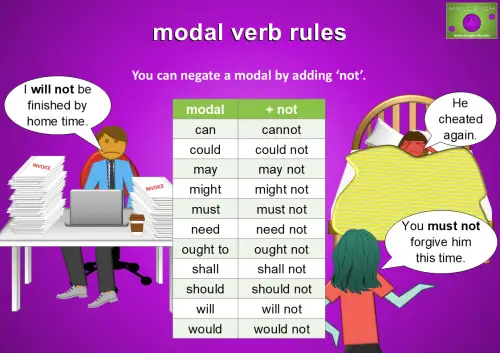
You can negate a modal by adding ‘not’.
For example:
- I will not be finished by home time.
- He cheated again.
You must not forgive him this time.
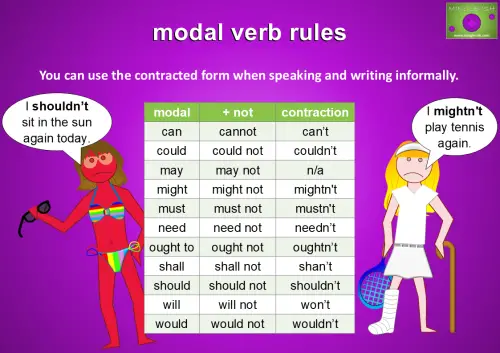
You can use the contracted form when speaking and writing informally.
For example:
- I shouldn’t sit in the sun again today.
- I mightn’t play tennis again.
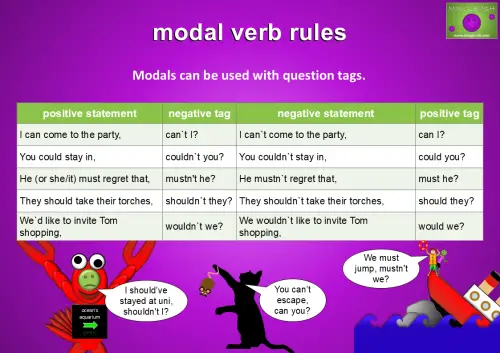
Modals can be used with question tags.
For example:
- I can come to the party, can`t I?
- He mustn`t regret that, must he?
- They should take their torches, shouldn`t they?
Modal Verbs – a Quick Summary
Modal verbs are a key part of English grammar, helping you express ability, possibility, necessity, and much more. Whether it’s can, should, or must, these versatile words help fine-tune what you want to say. Use them to give advice, make requests, or show probability – they’re perfect for everyday conversations.
To use them effectively, keep it straightforward. Match the modal to your purpose and practise with real-life examples to build confidence. Be sure to explore our other pages for a deeper dive into each modal verb and sharpen your English even further!
modal verbs quizzes
Now it’s time to test your understanding of modal verbs with these quick quizzes and see how well you know how to use them in everyday English.
further study
For more insights into the world of verbs, be sure to explore our other pages! Whether you’re learning about different verb tenses, phrasal verbs, helping verbs, or other types of verbs, we’ve got plenty of helpful resources to support your learning. Dive into these topics to enhance your grammar skills and take your English to the next level!