Adverb definition – What is an adverb?
Let’s kick-off this adverbs in English page by explaining what the definition of an adverb is… Am I right in thinking that you were taught that an adverb modifies a verb and ends in ‘ly’? Although this is correct, adverbs go much deeper than that. Adverbs of manner tend to end in ‘ly’, but guess what? There is more than one type of adverb which we’ll go into later.
Firstly, they are one of the ‘parts of speech’. Their function is to provide information about how, how often, when, or where something happens. Adverbs can modify adjectives, other adverbs, determiners, clauses, prepositions, verbs or sentences.
The function of adverbs is to provide information about how, how often, when, or where something happens.
- adverbs of frequency – how often the action is performed
- adverbs of time – when the action is performed
- adverbs of manner – how the action is performed
- adverbs of place – where the action is performed
FUN FACT: There are over 250 adverbs in English. Some words however are not always used as an adverb (depending on the sentence construction). They can be adjectives, conjunctions, interjections, nouns, prepositions, or pronouns.
adverbs in English examples
Right, let’s start learning adverbs. I’ll kick off with some easy examples:
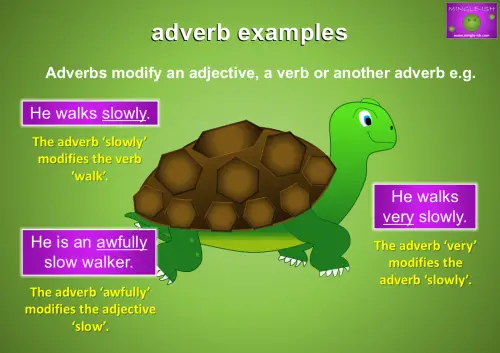
- He walks slowly – the adverb ‘slowly’ modifies the verb ‘walk’.
- He walks very slowly – the adverb ‘very’ modifies the adverb ‘slowly’
- He is an awfully slow walker – the adverb ‘awfully’ modifies the adjective ‘slow’.
- He plays excellently – the adverb ‘excellently’ modifies the verb ‘play’.
- He plays incredibly excellent – the adverb ‘incredibly’ modifies the adverb ‘excellently’
- He is an extremely excellent player – the adverb ‘extremely’ modifies the adjective ‘excellent’.
adverbs that modify verbs
You’ve seen some examples of adverbs in use, let’s delve deeper… When an adverb modifies a verb, it usually tells us how, when, where, in what manner, or to what extent the action is performed.
For example:
- how – He ran quickly.
- where – He ran there.
- manner – He ran naked.
- when – He ran earlier.
- extent – He ran fastest.
So you get the idea. Let’s take a look at a few more examples of adverbs modifying verbs. Remember, verbs are action words.
- I’m thoroughly cleaning the windows.
This shows how the windows are cleaned. - He finally proposed.
This shows when he proposed.
- He’ll sleep eventually.
This shows when he’ll sleep. - It always snows.
This shows how often it snows.
- I’m waiting patiently for the bus.
This shows in what manner I am waiting for the bus. - I wish I worked outside.
This shows where I wish I worked.
- I highly recommend this book.
This shows to what extent i recommend this book. - I’ve looked everywhere for my glasses.
This shows where I have looked for my glasses.
adverbs that modify adjectives
Adverbs can also modify adjectives. The purpose is to add a degree of intensity to the adjective.
For example:
- He is a very fast runner.
The adverb ‘very’ is modifying the adjective ‘fast’. - His shoes are surprisingly red.
The adverb ‘surprisingly’ is modifying the adjective ‘red’. - The race is really difficult.
The adverb ‘really’ is modifying the adjective ‘difficult’. - He looks extremely tired.
The adverb ‘extremely’ is modifying the adjective ‘tired’.
Let’s take a look at some more examples.
- I’m extremely good at painting.
The adverb ‘extremely’ is modifying the adjective ‘good’. - She’s simply greedy.
The adverb ‘simply is modifying the adjective ‘greedy’.
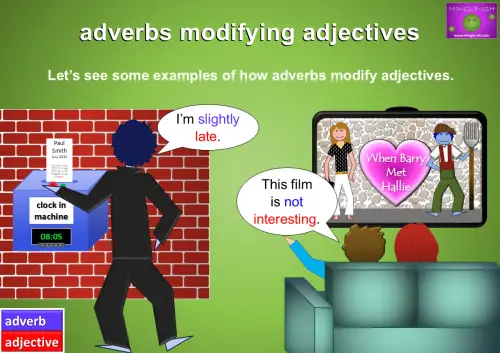
- I’m slightly late.
The adverb ‘slightly’ is modifying the adjective ‘late’. - This film is not interesting.
The adverb ‘not’ is modifying the adjective ‘interesting’.
- This drink is truly delicious.
The adverb ‘truly’ is modifying the adjective ‘delicious’. - I’m utterly devastated about losing a dear friend.
The adverb ‘utterly’ is modifying the adjective ‘devastated’.
adverbs that modify other adverbs
Adverbs can also modify other adverbs. The purpose is to add a degree of intensity to the adverb.
For example:
- He is running very quickly.
The adverb ‘very’ is modifying the adverb ‘quickly’. - His shoes are very brightly coloured.
The adverb ‘very’ is modifying the adverb ‘brightly’. - The race is just too difficult.
The adverb ‘just’ is modifying the adverb ‘too’. - He looks quite incredibly tired.
The adverb ‘quite’ is modifying the adverb ‘incredibly’.
Let’s take a look at some more examples.
- I almost always bake on Friday.
The adverb ‘always’ is modifying the adverb ‘bake’. - I very rarely catch one this big.
The adverb ‘very’ is modifying the adverb ‘rarely’.
- I can run remarkably quickly.
The adverb ‘remarkably’ is modifying the adverb ‘quickly’. - He’s doing that rather easily.
The adverb ‘rather’ is modifying the adverb ‘easily’.
- You drive unusually slowly.
The adverb ‘unusually’ is modifying the adverb ‘slowly’. - I train exceptionally hard.
The adverb ‘exceptionally’ is modifying the adverb ‘hard’.
different types of adverbs
Now you know what an adverb does and how to spot one. Let’s look a little deeper into the different types of adverbs including:
- adverbs of frequency
- adverbs of time
- adverbs of manner
- adverbs of place
Click on the links below to learn about the different types of adverbs in English with picture examples.
Adverbs make sentences clearer and more interesting by showing how, when, where, or how much something happens. Keep practising, and you’ll use them naturally.
Did you enjoy this page on adverbs in English? Want to keep going on your grammar learning quest? Well, good news – there are plenty more topics to sink your teeth into! Head to my grammar section now and get cracking.